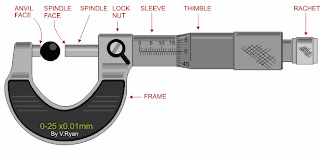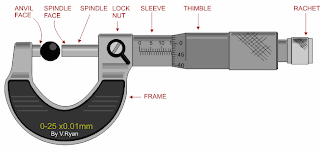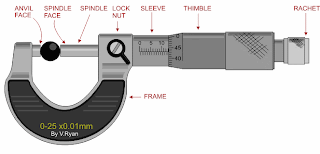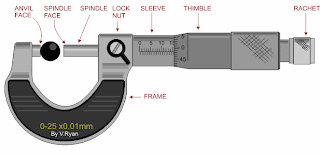

Using the first example seen below:
1. Read the scale on the sleeve. The example clearly shows12 mm divisions.
2. Still reading the scale on the sleeve, a further ½ mm (0.5) measurement can be seen on the bottom half of the scale. The measurement now reads 12.5mm.
3. Finally, the thimble scale shows 16 full divisions (these are hundredths of a mm).
The final measurement is 12.5mm + 0.16mm = 12.66
other example
Sleeves full read = 16 mm
Sleeves 1/2 read = 0 mm
Timble read = 0.35 mm
Total Measurement = 16.35 mm




